|
|
|
Title
|
|
Over-expression of ERT(ESX/ESE-1/ELF3), an ets-related transcription factor, induces endogenous TGF-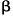 type II receptor expression and restores the TGF- type II receptor expression and restores the TGF-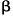 signaling pathway in Hs578t human breast cancer cells signaling pathway in Hs578t human breast cancer cells
|
 |
|
Jay Chang, Cecile Lee, Ki-Baik Hahm, Youngsuk Yi, Shin-Geon Choi & Seong-Jin Kim
Laboratory of Cell Regulation and Carcinogenesis, National Cancer Institute, NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, MD 20892-5055, USA
Correspondence to: Seong-Jin Kim, Laboratory of Cell Regulation and Carcinogenesis, National Cancer Institute, NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, MD 20892-5055, USA
|
|
Abstract
|
 |
The epithelium-specific transcription factor, ERT/ESX/ESE-1/ELF3, binds to the TGF-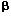 RII promoter in a sequence specific manner and regulates its expression. In this study, we investigated whether ERT could regulate endogenous TGF- RII promoter in a sequence specific manner and regulates its expression. In this study, we investigated whether ERT could regulate endogenous TGF-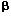 RII expression in Hs578t breast cancer cells. Analyses of the Hs578t parental cell line revealed low RII mRNA expression and resistance to the growth inhibitory effects of TGF- RII expression in Hs578t breast cancer cells. Analyses of the Hs578t parental cell line revealed low RII mRNA expression and resistance to the growth inhibitory effects of TGF-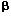 . Infection of this cell line with a retroviral construct expressing ERT induced higher levels of endogenous RII mRNA expression and protein expression relative to cells infected with chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CATneo) as a control. Relative to control cells, the ERTneo-expressing Hs578t cells show approximately a 50% reduction in cell growth in the presence of exogenous TGF- . Infection of this cell line with a retroviral construct expressing ERT induced higher levels of endogenous RII mRNA expression and protein expression relative to cells infected with chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CATneo) as a control. Relative to control cells, the ERTneo-expressing Hs578t cells show approximately a 50% reduction in cell growth in the presence of exogenous TGF-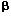 1, as well as a fourfold higher induction of activation in transient transfection assays using the 3TP-luciferase reporter construct. When transplanted into athymic mice, ERT-expressing Hs578t cells showed decreased and delayed tumorigenicity compared with control cells. This data strongly suggests that ERT plays an important role as a transcriptional activator of TGF- 1, as well as a fourfold higher induction of activation in transient transfection assays using the 3TP-luciferase reporter construct. When transplanted into athymic mice, ERT-expressing Hs578t cells showed decreased and delayed tumorigenicity compared with control cells. This data strongly suggests that ERT plays an important role as a transcriptional activator of TGF-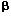 RII expression, and that deregulated ERT expression may play a critical role in rendering Hs578t human breast cancer cells insensitive to TGF- RII expression, and that deregulated ERT expression may play a critical role in rendering Hs578t human breast cancer cells insensitive to TGF-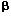 ‘s growth inhibitory effects. Oncogene (2000) 19, 151 – 154. ‘s growth inhibitory effects. Oncogene (2000) 19, 151 – 154.
|
 |
| Keywords |
 |
transcription factor; cancer; TGF-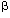 ; ; ; tumorigenicity ; ; ; tumorigenicity
|
 |
|
Received 9 August 1999; Revised 16 September 1999; Accepted 28 September 1999

©
Macmillan Publishers Ltd 2000
|
|
|