|
|
|
Title
|
|
Modulation of ara-CTP levels by fludarabine and hydroxyurea in leukemic cells
|
 |
|
M Ahlmann, C Lanvers, K Lümkemann, C Rössig, A Freund, M Baumann & J Boos
Department of Pediatric Oncology, University of Münster, Albert Schweitzer Str. 33, 48129 Münster, Germany
Correspondence to: J Boos, Fax: (0)251–83–47828
|
|
Abstract
|
 |
The rate of ara-cytosine triphosphate (ara-CTP) accumulation and its retention has been correlated with 1-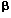 -D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C)-mediated toxicity and clinical outcome in childhood and adult leukemia. We tested to what extent preincubation with the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors fludarabine (F-ara-A) and hydroxyurea (HU) enhanced ara-CTP levels in two human myeloid (HL-60, CMK) and two lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines (MOLT-4, BLIN-1) and also in blasts from 28 children with acute leukemia (AML: 14, ALL: 14). Incubation experiments carried out with cell lines showed F-ara-A and HU to be equipotent in increasing ara-CTP levels. The highest increase was observed in HL-60 cells whereas preincubation had no modulatory effect in MOLT-4 cells. Accordingly, modulation of intracellular ara-CTP levels differed between the subtypes of childhood acute leukemia: whereas in T-ALL (five) preincubation with F-ara-A and HU had no effect on intracellular ara-C metabolism, increased ara-CTP levels were seen in some cases of pre-B-ALL (seven). In myelogenous blasts (12) clinically relevant enhancement of ara-C toxification was regularly obtained with both, F-ara-A (1.9-fold) and HU (1.5-fold). In conclusion, our data suggest that combinations of ara-C and ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors are apt to increase ara-CTP levels depending on the individual cell type and its sensitivity towards ara-C modulators. Leukemia (2001) 15, 69–73. -D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ara-C)-mediated toxicity and clinical outcome in childhood and adult leukemia. We tested to what extent preincubation with the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors fludarabine (F-ara-A) and hydroxyurea (HU) enhanced ara-CTP levels in two human myeloid (HL-60, CMK) and two lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines (MOLT-4, BLIN-1) and also in blasts from 28 children with acute leukemia (AML: 14, ALL: 14). Incubation experiments carried out with cell lines showed F-ara-A and HU to be equipotent in increasing ara-CTP levels. The highest increase was observed in HL-60 cells whereas preincubation had no modulatory effect in MOLT-4 cells. Accordingly, modulation of intracellular ara-CTP levels differed between the subtypes of childhood acute leukemia: whereas in T-ALL (five) preincubation with F-ara-A and HU had no effect on intracellular ara-C metabolism, increased ara-CTP levels were seen in some cases of pre-B-ALL (seven). In myelogenous blasts (12) clinically relevant enhancement of ara-C toxification was regularly obtained with both, F-ara-A (1.9-fold) and HU (1.5-fold). In conclusion, our data suggest that combinations of ara-C and ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors are apt to increase ara-CTP levels depending on the individual cell type and its sensitivity towards ara-C modulators. Leukemia (2001) 15, 69–73.
|
 |
| Keywords |
 |
|
hydroxyurea; fludarabine; acute leukemia; cytarabine; ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors
|
 |
|
Received 2 June 2000; Accepted 31 August 2000

©
Macmillan Publishers Ltd 2001
|
|
|